PLEASE MATCH YOUR ASSIGNMENT QUESTIONS ACCORDING TO YOUR SESSION
CHE-01 (January 2025 – December 2025) Assignment Questions
1. a) Describe the common features which can be explained by the theoretical model of Bohr? Briefly write the limitation of this model.
b) Calculate the ionization energy of hydrogen atom using Bohr’s theory.
2. a) Derive an expression for calculating energy values corresponding n = 3 for a particle in one dimensional box.
b) Write the values of four quantum numbers for 3d electrons.
3. a) Explain the reason for the variation of the first ionization energies of the third period elements.
b) Calculate the lattice energy (in Units kJ mol-1 ) for ZnO crystal using Eq. 3.4 based on electrostatic model and using a Born-Haber cycle. Compare the two answers and comment on any difference. Useful data:
Medelung constant (A) = 1.6411
Born Constant (n) = 8
Internuclear distance (a) = 199 pm
4. a) In carbonate ion, all the three CO bonds have identical bond length. Explain.
b) Explain the type of hybridization in phosphorous pentafluoride.
5. a) By writing molecular orbital configuration for each of following molecules calculate the bond order and also determine whether it is paramagnetic or diamagnetic.
b) Using suitable examples define gerade and ungerade orbitals.
b) Determine the wavelength for a transition from the v = 0 to the v = 1 level. Is this transition in the IR region of the electromagnetic spectrum?
c) Which of the following molecules exhibit rotational and or vibrational spectra H2, HF, CO, NO
8. a) From the infrared spectrum given below, identify the possible functional groups corresponding to the peaks indicated by the arrows.
b) Explain why ![]() transitions are the most useful transition in UV-VIS spectroscopy?
transitions are the most useful transition in UV-VIS spectroscopy?
c) UV-VIS absorption spectra are broad band spectra. Explain.
9. a) Normal water contains isotope of hydrogen 3H, tritium. It has a half-life of 12.3 years. Determine the age of a bottle of wine whose 3H radiations is about 1/10 that present in new wine.
b) Complete following equation
10. a) Arrive at the Lewis structure of XeF4 using the steps given in Unit 3.
b) Predict the hybridization state of each carbon atom in allene which has the following structure:
CHE-01 (January 2024 – December 2024) Assignment Questions
1. a) Calculate the ionisation energy of rubidium per atom, if light of wavelength 5.84 x 10-8 m produces electrons with a speed of 2.450 x 106 ms-1.
[Hint: Assume that the threshold frequency refers to the frequency corresponding to the ionisation energy.]
b) Assume that the electron in Li2+ ion is in third orbit. Calculate
i) the radius of the orbit, and
ii) the total energy of the electron
[Hint: Li2+ ion also has atomic spectra similar to hydrogen atom. while applying relevant equations, use Z = 3.]
2. Using steps 1 to 5 given in Sec. 3.7 of Unit 3, draw the Lewis structures of BrF5 and XeF2. Using VSEPR theory, predict their shapes.
3. Calculate the number of normal modes of vibration of BrF5 and XeF2. Draw diagrams to illustrate the symmetric stretching, asymmetric stretching and bending vibrations of XeF2.
4. a) You are provided with pure copper sulphate crystal. Using Beer-Lambert law, how can you determine the concentration of a test solution of copper sulphate? Explain in a detailed way.
b) What is the essential condition for a molecule to be microwave active? Classify the following molecules as microwave active or microwave inactive and state the reason in each case.
NO, Br2, N2O, XeF2
[Hint: N2O is a linear molecule and one of the nitrogen atoms is at the centre.]
5. a) For 1H19F, the lowest wave number absorption line in its rotational spectrum occurs at 41.11 cm-1. Calculate the wave numbers corresponding to its second, third and fourth absorption lines. Explain the term, rotational spacing using these values.
b) i) Based on Subsec. 6.6.3, draw a rough sketch of PM vs. T-1 curves for BF3 and NH3.
ii) Which of the two, BF3 and NH3, has a nonzero value for orientation polarization? State the reason.
6. Explain the following terms:
a) Moderator
b) Breeder reactor
c) Nuclear fusion
d) Transmutation reaction
e) Tracer technique
7. a) Draw the enantiomers for 2, 3-dibromopentane. Identify at least one pair of diastereomers among these structures. Can it form meso form? State the reason for your answer.
b) Explain one application each for the study of paramagnetic and diamagnetic substances sing magnetic susceptibility measurements. Comment on their dependence of these values of temperature.
8. a) State the modification that was needed for Bohr’s atom model in view of Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle.
b) Explain the need to introduce normalization constant and, complex conjugate of wave function.
c) Using Table 2.2, and the equation given in Eq. 2.54 of Unit 2, explain the directorial characteristics of 2px and 3dxz orbitals of a species with one electron.
9. a) On the basis of molecular orbital theory, draw the energy pattern for ![]() ion. Comment on the bond order. Is it paramagnetic? Explain.
ion. Comment on the bond order. Is it paramagnetic? Explain.
b) ![]() ion has less stable arrangement that H2 molecule. Explain using molecular orbital theory.
ion has less stable arrangement that H2 molecule. Explain using molecular orbital theory.
c) Explain with an example, the term, nonbonding molecular orbitals.
10. a) In the following compound, indicate the type of hybridization of each carbon atom. Also predict the carbon-carbon bond lengths using Table 4.4.
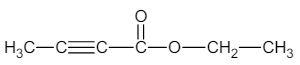
b) Explain, using hybridization theory and diagram, the structure of allene, CH2 = C = CH2.











