PLEASE MATCH YOUR ASSIGNMENT QUESTIONS ACCORDING TO YOUR SESSION
IGNOU CHE-06 (January 2025 – December 2025) Assignment Questions
1. a) List the factors that are responsible for the relative strength of nucleophiles. Write the conjugate acids of the following nucleophiles.
b) Categorise the following reactions as oxidation or reduction reaction indicating the oxidation state of carbon in the reactants and the products for all the reactions:
2. a) What is the principle of microscopic reversibility? How is it explained by the transition state theory of organic reactions? Explain with the help of an example.
b) Why is a substitution reaction proceeding by SN2 mechanism referred sometimes as direct displacement process? Arrange the following aliphatic bromides in the increasing order of reactivity by SN2 mechanism:
3. a) Answer the questions given for the following reaction:
i) Write the electrophile participating in this reaction.
ii) Write the reagents used for the reaction.
iii) Name the reaction.
iv) Write the complete mechanism of the reaction.
b) Which of the following pair of carbocation is more stable and why?
4. a) Explain the following:
i) Electron withdrawing substituents at the carbonyl carbon increase the reactivity towards nucleophilic addition reactions.
ii) Rate of reaction of acetaldehyde with aniline increases with the increase in acidity but beyond certain limit it decreases with further increase of acidity.
b) Differentiate Saytzeff and Hofmann rules giving suitable examples.
5. a) Predict the product(s) and give the mechanism of the following reactions:
b) Write short notes on the following giving mechanism:
i) Aldol condensation
ii) Michael addition
6. Write the chemical reaction for the following reactions along with their detail description:
a) Reimer-Tiemann reaction
b) Carbylamine reaction
c) Witting reaction
d) Wolff rearrangement
e) Hofmann rearrangement
7. a) Explain, why the reaction of m-bromoanisole with sodamide gives only one product.
b) Describe the bromination reactions at allylic and benzylic positions by N-bromosuccinimide.
8. a) Write detail mechanism for the following rearrangements:
i) Wagner-Meerwein rearrangement
ii) Beckmann rearrangement
b) Explain the mechanism of [4+2] cycloaddition reaction.
CHE-06 (January 2024 – December 2024) Assignment Questions
1. a) Which of the carbocation is more stable in the following pairs and why?
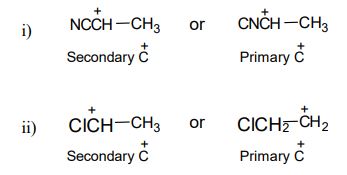
b) Explain the following:
i) Enol form does not react with water to give diol.
ii) Fluorine and iodine generally do not react with alkene or alkyne.
iii) Hydroboration looks like an anti-Markownikowf’s addition.
2. Explain the following:
a) Electron withdrawing substituents at the carbonyl carbon increases the reactivity towards nucleophilic addition reactions.
b) Reaction of hydrocyanic acid and benzaldehyde is very slow, but become fast when cyanide ion is added.
3. a) Explain isotope effect in E2 elimination reaction with suitable example.
b) Differentiate Saytzeff and Hofmann rules giving suitable examples.
4. a) State oxidation state. Calculate the oxidation state of carbon atom of CCl4.
b) Predict the product(s) and give the mechanism of the following reactions:
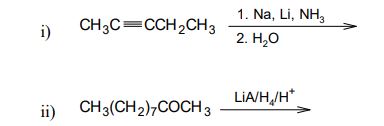
5. Write short note on the following: (Give mechanism)
a) Aldol condensation
b) Michael addition
6. Write the chemical reaction for the following reactions along with their detail description:
a) Reimer-Tiemann reaction
b) Carbylamine reaction
c) Wittig reaction
d) Wolf rearrangement
7. a) Explain, why the reaction of m-bromoanisole with sodamide gives only one product.
b) Describe the bromination reaction at alkylic and benzylic position by N-bromosuccinimide.
8. a) Write detail mechanism for the following rearrangements:
i) Wagner-Meerwein rearrangement
ii) Backmann rearrangement
b) Explain the mechanism of [4+2] cycloaddition.
9. a) Taking suitable examples, explain the role of sensitisers in photo reactions.
b) Describe reaction types used to construct a carbon skeleton with suitable examples.
10. Write short notes on:
a) Cleaning action of soaps
b) Auxochromes
c) Antibiotics
d) Condensation polymers
e) Retrosynthesis














